The Primary Impact of Predictive Maintenance.
The impact of predictive maintenance across various industry sectors has been extensively documented in recent years. This article explores how manufacturing companies can achieve significant cost savings by minimizing downtime, ultimately improving their financial investments. We present practical examples and key statistics that highlight the financial benefits of permanent monitoring. Additionally, we analyze insights from the Siemens report [1], offering our perspective on its findings.
Alongside downtime reduction, permanent monitoring can also boost productivity, extend equipment life, improve efficiency, enhance safety, and optimize resource use.
Over the past decade, many industries have embraced advanced technologies that boost productivity, but with increased complexity comes greater risk. Frequent equipment failures and subpar maintenance drive costly downtime. Forward-thinking companies mitigate this by adopting a data-driven approach that minimizes disruption and maximizes efficiency. But others still cling to outdated, reactive strategies, which require manual intervention to identify, diagnose and repair problems. While predictive maintenance requires an upfront investment, the long-term savings and reliability gains are substantial.
The True Cost of Downtime
Every industry faces its own distinct challenges, yet the financial impact of downtime remains significant and costly. [1]
- Power: $2.4M/hour
- Automotive: $2M/hour
- Heavy Industry (Steel, Cement, etc.): $240K/hour
- Logistics: $100K/hour
- Oil & Gas: $50K/hour
- FMCG: $40K/hour
Given these high figures, companies can no longer afford to take risks with outdated and reactive maintenance strategies.
The Inherent Risks Around Reactive Maintenance
Reactive maintenance is like stopping the leak after the flood. Too little, too late. By the time an issue is discovered, it’s too late to prevent major consequences such as lost production, damaged equipment, high contract penalties, wasted resources, and even complete or partial shutdown.
And yet, most failures aren’t random. They build up over time until they escalate in a critical breakdown. Without predictive monitoring, small problems like unnoticed bearing wear, minor leaks, and slight inefficiencies can snowball into full-scale operational issues. There’s a knock-on effect, too. Repairs take longer and cost more, significantly disrupting operations.
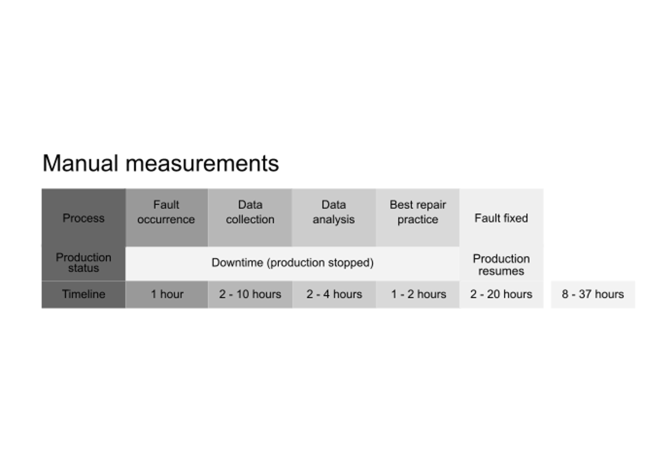
The Cost of Reactivity
• Slow Troubleshooting: Engineers waste hours locating and diagnosing issues.
• Safety Risks: Large plants, tight spaces, and hazardous zones make manual inspections slow and dangerous.
• Restart Delays: Even after repairs, systems take time to reset. On average, this can take between 50 to 70 minutes [2]. In heavy industries like steel and cement, re-heating of furnaces can take days.
• Environmental Waste: Energy waste increases when production lines go down due to inefficient restarts and idle equipment. Extra energy is also required to regain efficiency, leading to higher CO2 emissions.
A practical example: Leaking Traps
Not all issues cause a production shutdown. But even small failures can lead to significant costs. Take steam traps, for example.
A faulty steam trap may appear to function correctly, but if it leaks, it reduces process efficiency, wastes energy, increases water consumption, and raises CO2 emissions.
Now, consider a plant with 4,000 steam traps. Depending on maintenance frequency, the annual failure rate can range from 10% to 30%. Steam generation costs vary by country and heating resource, but assuming a conservative estimate of €8 per 1,000 kg of steam, a single leaking trap losing 384 kg daily results in a total daily loss of €1,229. Annually, this amounts to approximately €448,000 [3].
So, investing in a permanent monitoring system can quickly pay for itself, delivering a return on investment within months.
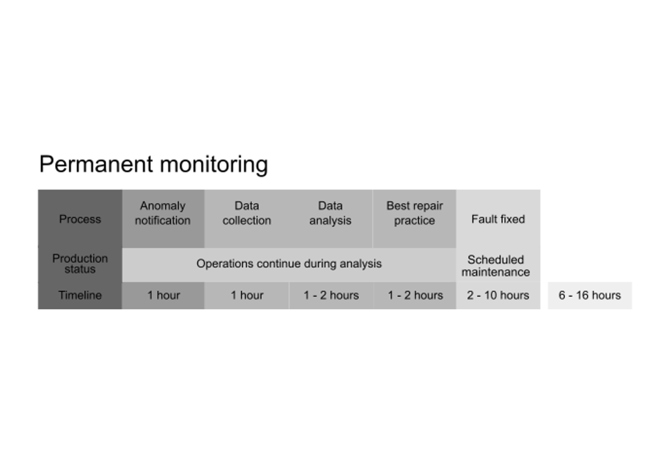
Predictive Maintenance: A Smarter Approach
Predictive maintenance is transformative. Rather than responding to equipment failures, companies can prevent them. Through continuous monitoring via sensors, equipment health is assessed in near real-time, ensuring engineers are kept informed and enabling the identification of potential issues before they escalate. Ultimately, it is a visionary, game-changing solution:
- Instant Detection: Sensors pick up anomalies in near real-time, eliminating guesswork.
- Smarter Decision-Making: Engineers analyze data remotely before stepping into the field, reducing risks and delays.
- Proactive Repairs: Maintenance is scheduled when it causes the least disruption, keeping production flowing.
- Minimal Downtime: Teams arrive prepared with the right tools and spare parts, cutting repair times dramatically.
Of course, sudden critical failures or brief random events may still cause disruptions. But permanent monitoring offers an advantage by tracking anomalies, allowing engineers to analyze data and identify the cause of the failure.
Moreover, continuous monitoring collects near real-time data, enabling engineers to analyze trends and identify operational weaknesses. This allows them to enhance efficiency through recalibration, redesign, or replacing worn-out parts.
The Proof: Hard Data on Predictive Maintenance
The Siemens Report [1] confirms its substantial benefits:
- 85% better accuracy in forecasting downtime.
- 50% fewer unexpected shutdowns.
- 55% boost in maintenance team productivity.
- 40% lower maintenance costs.
Varying by industry, manufacturing companies typically face an average of 15 hours of unplanned downtime each month. By implementing permanent monitoring, they can reduce downtime significantly, delivering a consistent return on investment.
Estimated financial benefits: Downtime Reduction by Industry
- Power: $36M -> $4.3M saved
- Automotive: $30M -> $3.6M saved
- Heavy Industry: $3.6M -> $432K saved
- Logistics: $1.5M -> $180K saved
- Oil & Gas: $750K -> $90K saved
- FMCG: $600K -> $72K saved
A GE study [4] on the Oil and Gas industry also shows that permanent monitoring offers significant advantages over a reactive approach. Data-driven insights reduce unplanned downtime costs by 50% and reduce failure rates, as well as downtime frequency.
The Future is Predictive. The Future is Now.
Predictive maintenance is not a discretionary investment; it is an essential business strategy. Companies that fail to modernize risk substantial consequences, including revenue loss, elevated risks, and a growing disparity between themselves and their competitors.
By investing in near real-time monitoring, organizations can:
- Cut downtime and operational costs.
- Improve safety and efficiency.
- Extend equipment lifespan.
- Cut energy waste and CO2 emissions.
In conclusion, the integration of predictive maintenance is essential for organizations to remain competitive and optimize operational efficiency. By harnessing near real-time monitoring and data-driven insights, companies can effectively reduce downtime, enhance productivity, and drive significant cost savings.
Sources
[1] Siemens Report – The True Cost of Downtime 2024
[2] and [3] Figures calculated on data shared by our customer.
[4] General Electric Report – Digital Transformation in Oil & Gas.
